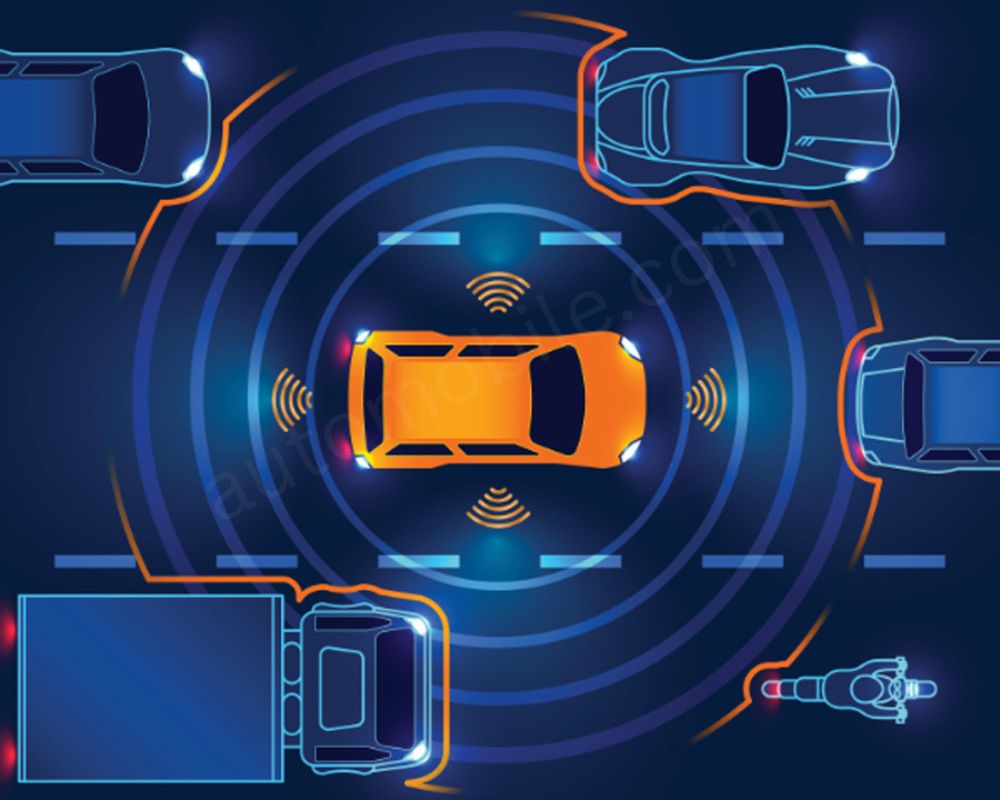
ADAS is changing the concept of car safety at an advanced level by giving a HUD of features that works like an attentive co-pilot. Adaptive driver assistance systems utilize a complex network of cameras, radar, and LiDAR sensors to monitor the environment, providing relevant information and sometimes even taking over to prevent accidents.
Why is ADAS necessary?
According to studies carried out by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration [US Department of Transportation, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration(.gov)], human error is the main cause of road crashes. Aspects such as fatigue, distraction, and the means of determination of the distance are diminished dramatically by the installation of ADAS. These systems are designed to be vigilant and detect potential hazards or take the appropriate actions when you are not at the top of your game, acting as an additional safety net while driving.
Expanding Your Awareness and Perception
Due to the limited field of view and blind spots on the road, drivers might face potential hazards. ADAS systems such as Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Blind Spot Detection (BSD) give you wider sensory perception and provide you with a better view of your surroundings. For example, a Rear Cross Traffic Alert system can alert you to approaching vehicles when reversing out of a parking space. Thus, it keeps you out of harm’s way during low-visibility conditions like foggy mornings or crowded parking lots.
Faster Than Human Reflexes
The most attentive driver cannot ever be 100% accident-free. When you have to react to immediate changes on the road, time is a problem, and this is where ADAS is very good. Rear-end and side collisions can be prevented by ADAS systems that immediately react with braking or steering corrections in milliseconds, perhaps avoiding the crash. Such immediate response may be just what you need in an emergency.
ADAS Features
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): The emergency protocol system serves as your guardian angel, overseeing you during emergencies. It perceives the situation where you are about to hit a stationary object or another vehicle and commands the braking of the vehicle to slow you down or bring you to a full stop. This can greatly limit the consequences of an accident as well as be able to totally prevent it, especially in heavy traffic or sudden stops.

- Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA): In your mind, picture having an encouraging gentle push to move on. LDW acts as A warning mechanism that gives you audio or visual feedback when you start to drift out of the lane without signaling. However, LKA goes a step further. The LDW mechanism can accomplish this through slowly and subtly turning the wheel to help you steer when a lane departure is detected.
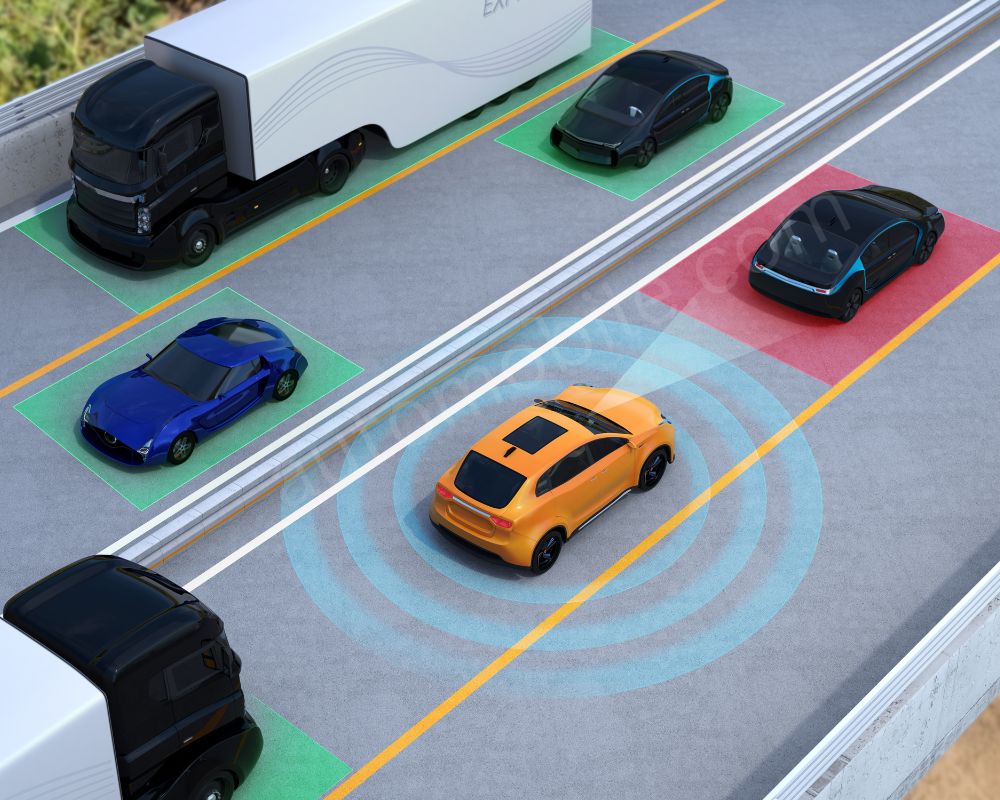

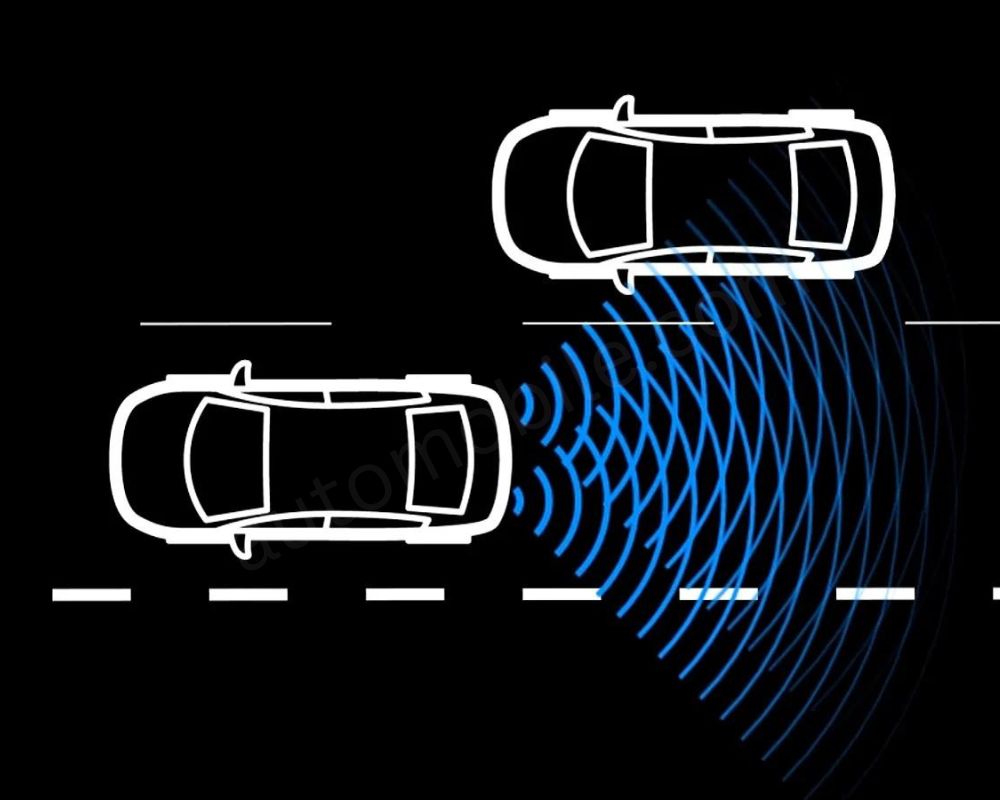
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): This option really comes in handy, especially when driving on highways, keeping the driver awake, fresh, and not bored during long journeys. ACC has a predetermined set following time which adjusts your speed according to that of the car in front of you. This provides some rest on longer trips and still maintains a safe distance in traffic.

- Blind Spot Detection (BSD): This is your second eye system, which becomes crucial when merging lanes. It recognizes vehicles in your blind spot, an area that unless you have a camera you can’t see through your mirror. BSD will provide a prompt if you are changing lanes without first looking or when another car is in your blind spot.
- Night Vision Assist: Poor visibility makes driving at night particularly hazardous. Night vision assist feature includes thermal imaging or infrared cameras to show the road ahead and illuminate pedestrians, animals, or other obstacles that might be difficult to spot with headlights alone. This results in you having time to react, thus averting the collision.
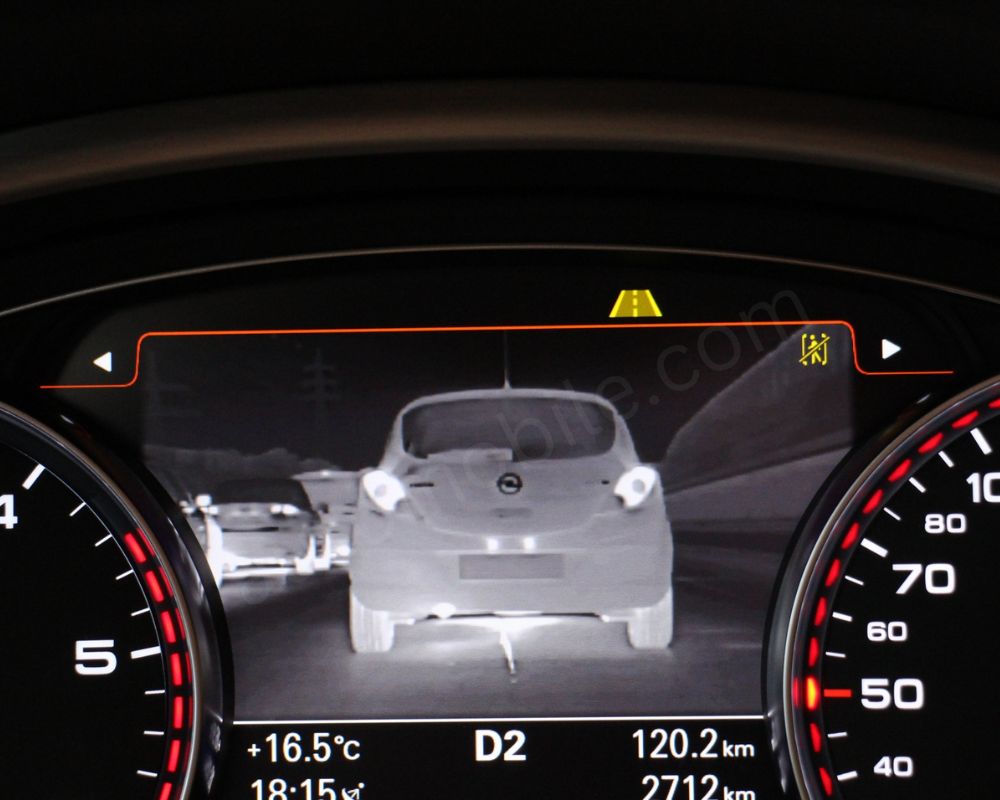

- Traffic Sign Recognition (TSR): No more missing critical road signs! TSR utilizes cameras to interpret traffic signs and displays them on your dashboard to inform speed limits, no passing zones, and other important road signs even when driving in an unfamiliar area.

- Parking Assist Systems: Parallel parking or dealing with narrow spaces may be difficult, but parking assist systems will do the job for you, even using cameras/sensors and so forth. These systems may give you visual or audible guidance or even take over the steering wheel to park the car for you, thus enabling you to park your car with ease.
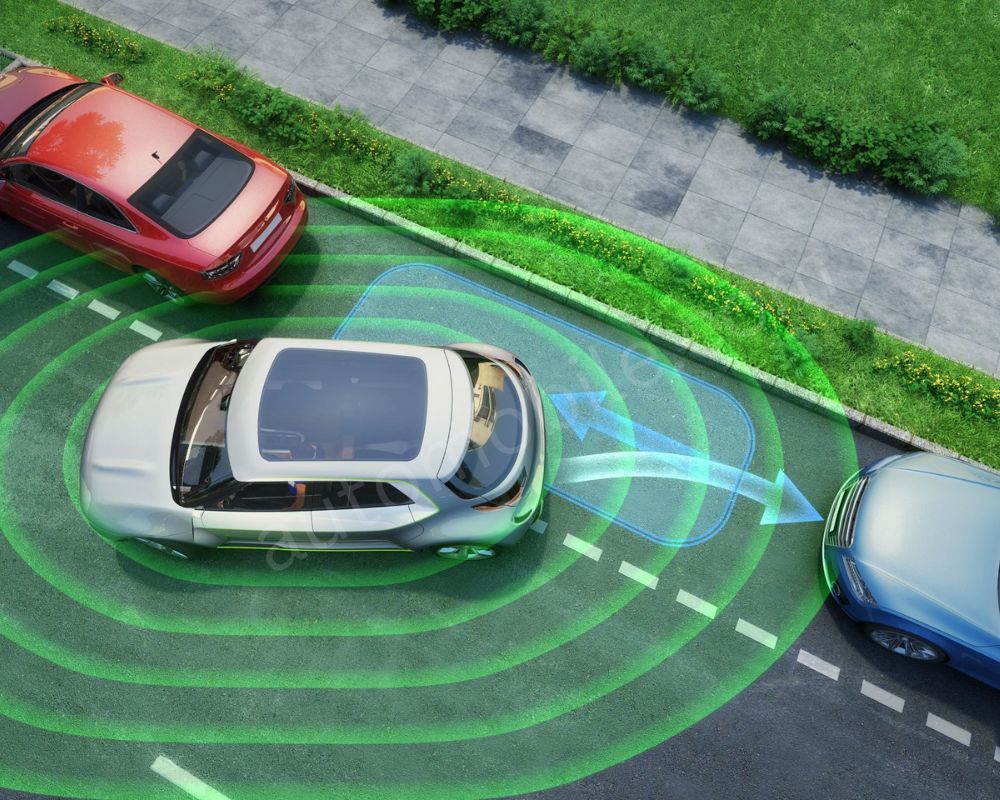

- Driver-Monitoring System (DMS): Driving skill can be severely hampered by drowsiness or fatigue. DMS employs cameras or other sensors to assess the driver’s awake level. If the system detects any signs of drowsiness, it can issue audible or visual warnings to call the driver’s attention, in a bid to avoid crashes caused by fatigued driving.

The purpose of the ADAS features is to support you and not to supersede your own safe driving skills. It’s essential to pay attention and maintain control of the vehicle all the time. However, with ADAS being your co-pilot, you are provided with an additional layer of security that can facilitate immediate actions and give you an advantage in the case of an unforeseen event, thus making your driving experience safer.

